One of the most important concepts, without which it is impossible to trade, is the time frame.
Let’s find out the time frame and how to use it. After reading this article, you will also learn how to use several time frames simultaneously in your trading, which can significantly increase your trading system's efficiency.
What is a Time Frame?
The time frame is the period of price movement.
For example, if the time frame is 5 minutes, it will mean that on the chart of the selected asset, you will see how the price changes every five minutes. Using a chart of Japanese Candlesticks or Bars means that a new candlestick/bar will appear on the chart every five minutes.
If the time frame is one day, a new candle or bar will appear every new trading day.
To trade successfully, you must first select the time frame in which you will use a trading strategy and which will receive signals from the trading system to open/close transactions.
This time frame is called the working time frame.
It should immediately be noted that the following rules apply when selecting a time frame:
The higher the time frame selected, the higher the accuracy of signals and the lower the risks.
The lower the time frame chosen, the lower the accuracy and the higher the risks.
The price trend is always stronger on higher time frames than on lower time frames. For example, if the price is moving up on the daily time frame (bullish trend), and the price is moving down on the 4-hour time frame of the same asset (bearish trend), the bullish trend will still be stronger than the bearish one.
What are the Main Forex Time Frames?
The key time frames in Forex are 1 minute, 5 minutes, 15 minutes, 30 minutes, 1 hour, 4 hours, one day, one week, and one month.
Each subsequent time frame is the most senior about the previous ones.
Each preceding time frame is the youngest concerning the succeeding ones.
It is generally accepted to conventionally divide the time frames into the following groups: low, medium, and high.
The low time frames are 1 minute, 5, and 15 minutes.
Middle time frames are 30 minutes, 1 hour, and 4 hours.
High time frames are one day, one week, and one month.

By analyzing the lower time frames, we analyze the short-term price behavior of an asset; by examining the medium-term time frames, we analyze the medium-term trend; and by analyzing the higher time frames, we see the long-term trend.
Which Time Frame is Best for Trading?
There is no concept of the best time frame for trading, as well as the concept of the best strategy for trading.
The choice of a time frame depends solely on the trader's subjective preferences – their temperament, their trading strategy, and the asset to be traded. It may happen in the market that some strategies working on low time frames may not work well on medium or high ones and vice versa. But the market is changeable. It also happens that the selected strategy stops working on the time frame chosen or asset. Then, the trader must decide whether to change the strategy, change the time frame, or abandon the analysis of that particular asset.
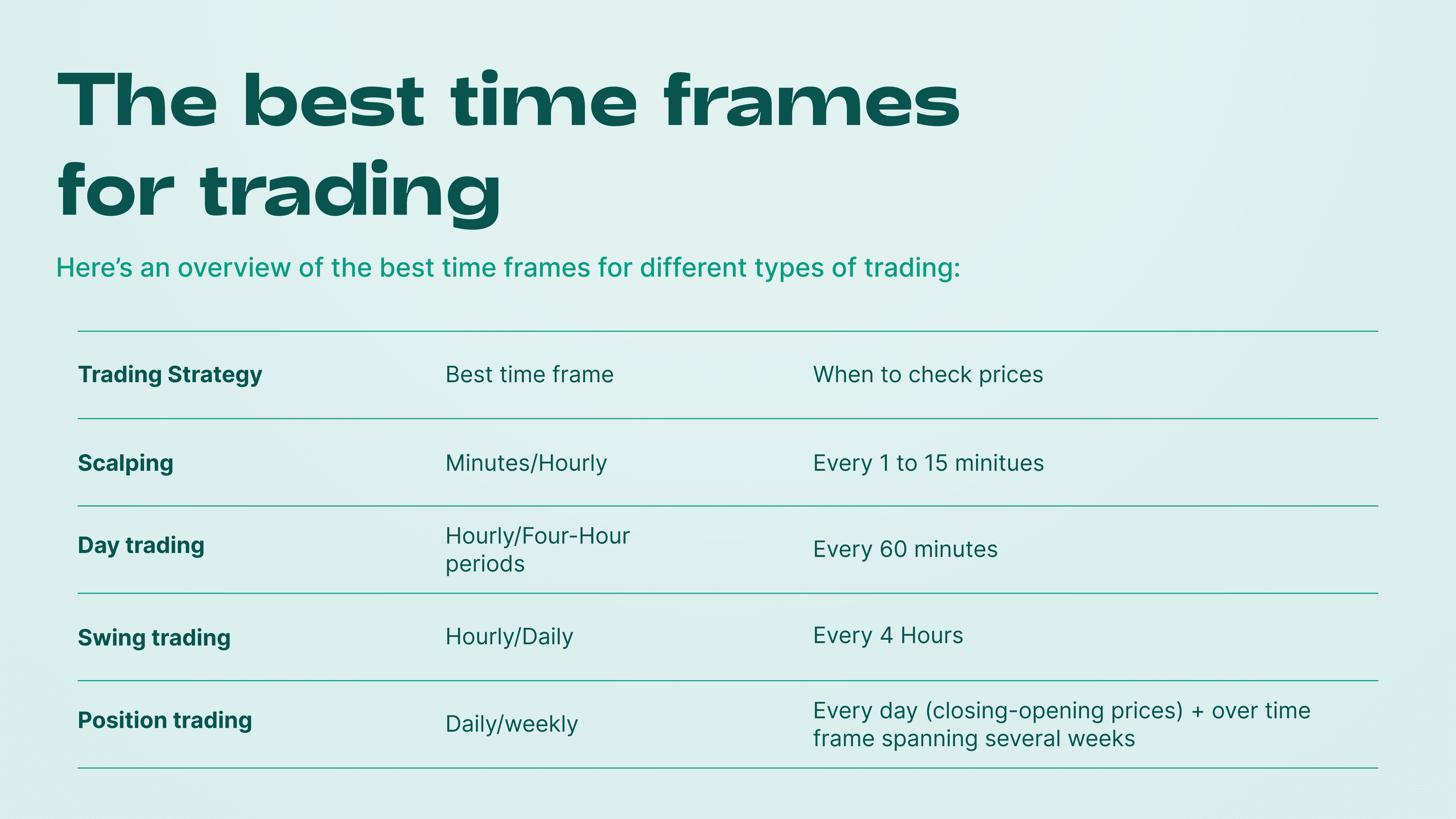
Best Time Frame for Scalping
Traders who trade on lower time frames are called scalpers.
Scalping is the riskiest approach in trading; naturally, it involves making the highest profits.
Scalpers try to earn on very short time frames of price movement and usually open and close big amounts of trades.
In our opinion, the best time frame for scalping is not 1 minute but 5 minutes. Scalping on 1 minute is too risky.
Best Time Frame for Day Trading
Day trading is a style of trading in which trades are opened and closed within one trading day. Traders who use this style are called day traders.
Day traders use mainly middle time frames, the most optimal of which is 1 hour.
Day traders take less risk than scalpers, and they never roll overnight.
Best Time Frame for Swing Trading
Swing trading is trading within one week.
Swing traders seek to catch intra-week price movements. Hence, their time frames are medium and high.
Optimal time frames for swing trading are 4 hours and one day.
Best Time Frame for Position Trading
Position trading involves the use of higher time frames.
This is the longest approach in trading.
The trades are open for several weeks and sometimes for several months.
In this case, the optimal time frames are one day and one week.
Multi-time frame analysis
Now, let’s see how to increase the efficiency of any trading system by using several time frames simultaneously.
Alexander Elder, a well-known technical analyst, suggested a three-screen system in which two-time frames should be used simultaneously to make a balanced decision. The first time frame is a working one. This is the time frame for a decision to open/close a position.
The second time frame is a checking one. It is the closest to the working time frame. Elder proposed to find the check time frame by multiplying the working time frame by 3, 4, or 5. For example, for a working time frame of 1 hour, the checking time frame would be one hour * 4 = 4 hours. For a time frame of 1 day, a check time-frame would be one day * 5 = 1 week.
Thus, each trading style will have its verifying time frame, or, as they say, trend time frame.
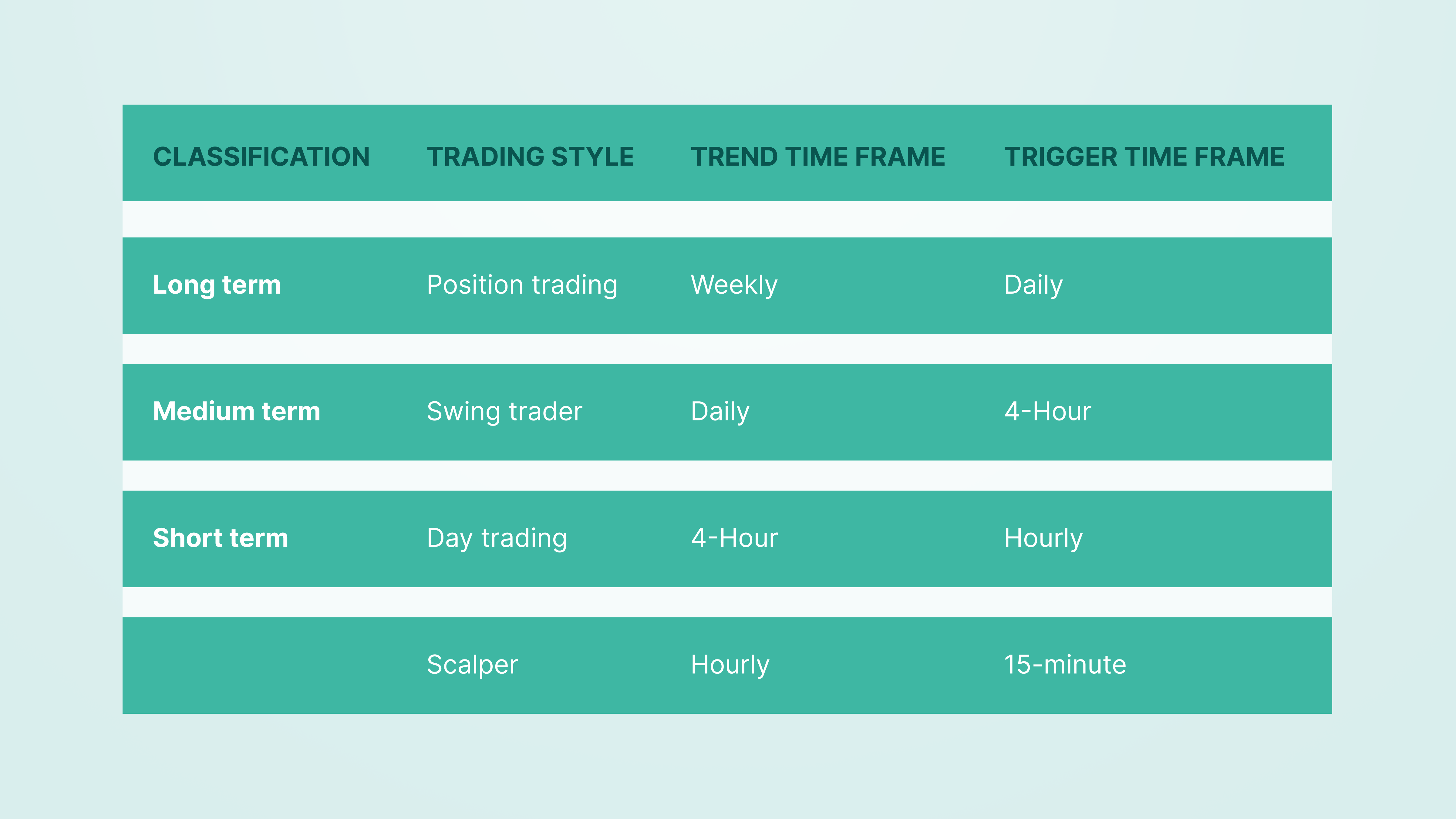
The basic principle of using two-time frames is that when opening a trade, the trends in both frames should not contradict each other.
For example, we are trading in the trend and will open a trade-up in the H1 time frame. In this case, in the H4 time frame, the trend must also be bullish. If the trend is bearish – it is better to refuse transaction opening.
Similarly, let's assume that the swing trader opens trade downwards on the D1 time frame, trading in the current trend’s direction. In this case, the movement must be bearish on the trend time frame W1.
Conclusion
Choosing and using a time frame correctly is the most essential part of any trading system.
Time frames give precious information about where the price can go and, therefore, are the best assistants for the trader.