How much will it cost you to trade on the Forex market? The most common way for a broker to ask a trader to pay a fee to trade on the currency market is spread. Here, we will explain how spreads work.
What is a spread?
A spread is a conventional concept for financial markets. It represents the difference between the lowest price sellers are willing to sell an asset and the highest price buyers would like to pay for this asset.
You have experienced spread when you came to a bank or an exchange office to get foreign currency. The bank always shows two quotes of currency – the one at which it agrees to buy it from you and the one at which it is ready to sell it to you. The spread between these two prices forms the bank’s revenue from the Foreign Exchange operations it performs for you.
Every asset has a bid and ask price. When you buy an asset, FBS opens your order at an ask price, and conversely, when you sell an asset, FBS opens your order at a bid price. Forex bid-ask spread is a fee for performing a trade. Smaller spreads mean better conditions for traders.
How does a bid-ask spread work?
There are two counterparts in financial markets: buyers and sellers. Buyers want to buy an asset at the lowest price possible. On the contrary, sellers want to sell an asset at the highest price. These two sides create a buying price called a bid and a selling price called an ask.
Spread is the difference between the bid and ask prices, so the Bid-Ask spread formula looks like this: Ask – Bid = Spread.
To sum up:
- The price we pay to buy the pair is called ask. It is always slightly above the market price;
- The price at which we sell the pair on Forex is called bid. It is always slightly below the market price;
- The price we see on the chart is always a bid price;
- The ask price is always higher than the bid price by a few tenths of a pip;
- Spread is the difference between these two prices.
SPREAD = ASK – BID
For example, the EUR/USD Bid/Ask currency rates are 1.12502/1.12506. You will buy the pair at the higher ask price of 1.12506 and sell it at the lower bid price of 1.12502. This represents a spread of 4 points.
Types of spread
The types of spread depend on the policy of the broker. A spread can be fixed or floating.
Fixed spreads
Fixed spreads remain the same no matter what market conditions are at any given time. That way, you know how much you will pay for a trade. Another good thing is that the broker won’t be able to widen the spread even if the market conditions change.
Floating spreads
Floating or variable spreads, on the contrary, are constantly changing. They will widen or tighten based on the supply and demand of currencies and overall market volatility. Floating spreads usually increase during important economic releases and bank holidays when the market's liquidity declines. However, when the market is calm, they can be lower than the fixed ones.
How to choose the optimal spread
The best thing you can do with your trading is to seek a broker with a low spread, as it’s the main gauge of fees you will pay for your trading activity. FBS provides amazing spreads for the most popular trading pairs, making it easy to trade without worry.
The optimal type of spread depends on your preferences as a trader. Generally, traders with smaller accounts who trade less frequently benefit from fixed spread pricing. Traders with larger accounts who frequently trade during peak market hours (when spreads are the tightest) and want fast trade execution will benefit from variable spreads.
Calculating costs
Note that the spread cost on Forex is usually negligible compared to the expenses on the stock or options markets. As the spread is quoted in points, a trader can easily calculate the cost of every trade by multiplying the spread in points by the value of 1 point.
Spread is an important parameter to consider when you choose a broker. Make sure that you are comfortable with the offered spreads. You can always test the company’s trading conditions by opening a demo account without investing your money.
The shorter the periods of your trade, the more important the size of a spread. For instance, if you hold a position open for several minutes and your gain is 1 pip, a 0.3-pip spread would mean paying 30% of your profit for executing this trade. If you keep your trade open for a day, there will likely be a bigger change in the price – let’s say you would earn 100 points. In that case, you will pay only 3% of your profit as a spread.
More popular currency pairs have smaller spreads. For example, the spread for EUR/USD trading is usually very small or, as traders say, tight.
How to check spread in MetaTrader
When you click the New Order button, a window appears where you can set the details of your trade. The window also shows the current bid and ask prices.
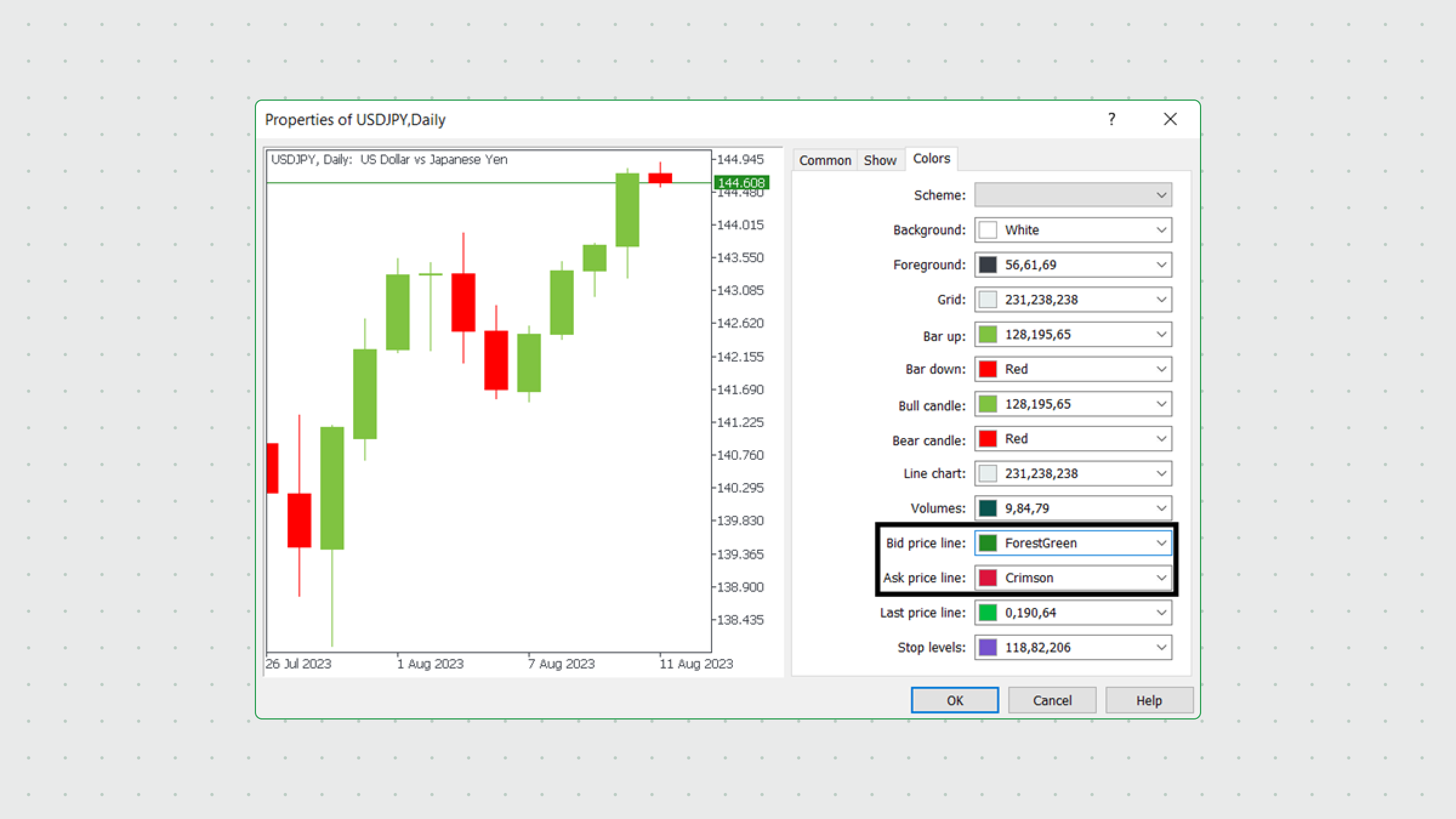
To add bid and ask lines to your chart, right-click anywhere on your chart and select Properties. Then click the Show tab and check the “Show ask price line” and “Show bid price line” boxes. Click the OK button, and the lines will appear in shorter time frames (in longer time frames, the bid line will cover the ask line).
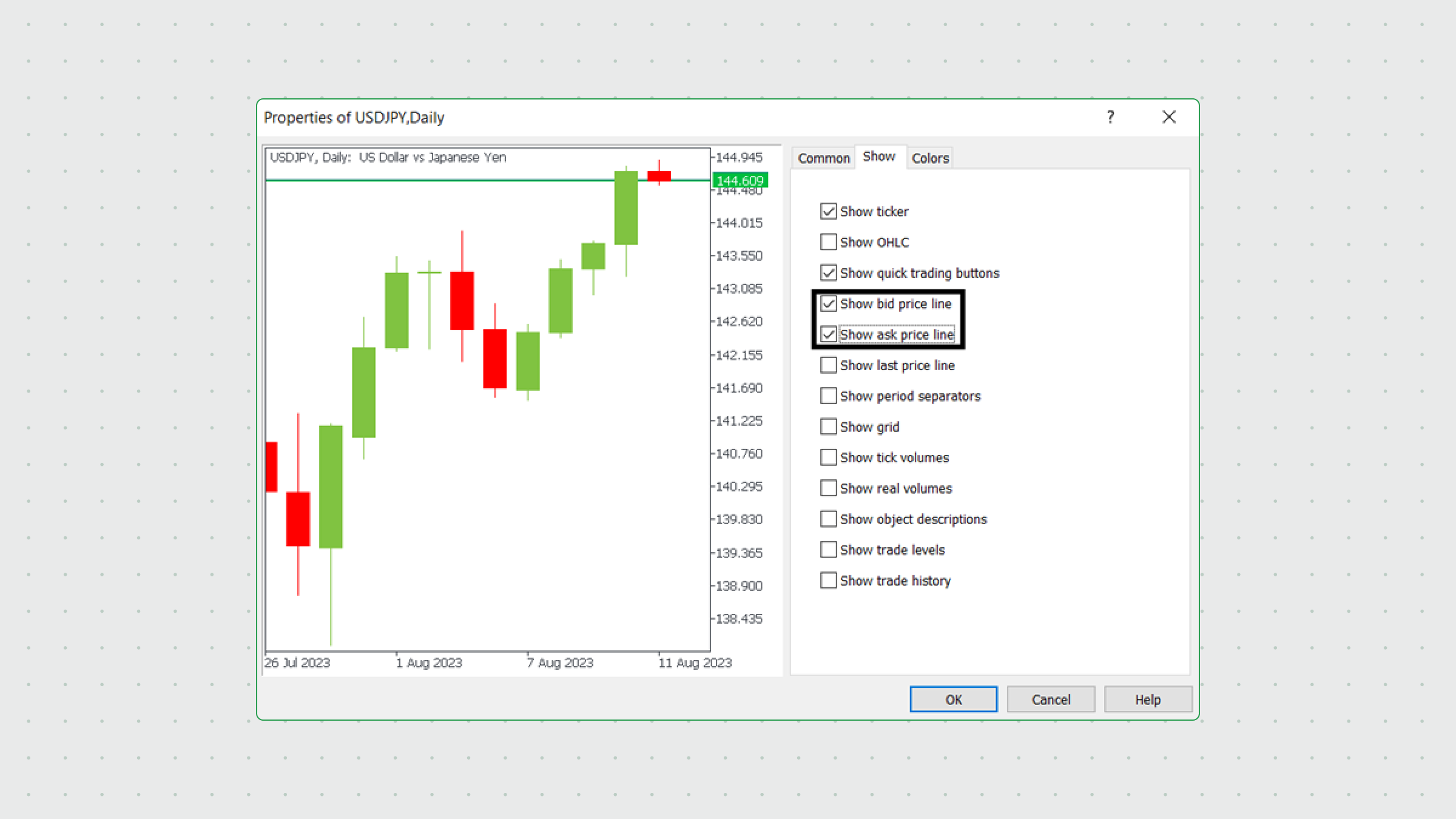
If you still cannot see the ask line, check if it is the right color. Return to your properties and check the lines’ colors.
You can also see the live bid/ask prices for all available trading instruments if you click View and then choose Market Watch.
What affects a spread’s size?
Sometimes, floating spreads can get very wide due to market fluctuations like important economic releases, news, or lack of swans (unexpected and greatly powerful events that may cause vast movements). As time passes, the spread tends to return to its normal state.
Exotic instruments may have high spreads, too. For example, USDTRY (US dollar to Turkish Lira) is an exotic instrument with a bigger-than-usual spread.
Finally, spreads widen when there is less liquidity on the market due to bank holidays.
Summary
The spread is a fee that traders pay to their broker for the opportunity to trade on the currency market. It represents the difference in the price at which a trader purchases or sells an underlying asset.
Spreads can be fixed or floating, and the best type of spread depends on the trader's preferences. If you trade more frequently, you are going to love tight spreads. Choosing a broker with low spreads is recommended to minimize the costs associated with trading and maximize the result.
Additionally, it's important to note that the spread is often quoted in points, the unit of price movement in Forex. Traders must understand the concept of spread and the different types of spreads offered by brokers to make informed trading decisions and manage their costs effectively.